Meshery Models
Introduction
Meshery is a cloud-native management plane that aims to provide a comprehensive set of tools for managing cloud-native applications and infrastructure. To achieve this, Meshery needs a model that can represent a wide range of constructs, from simple applications to complex microservices architectures. This document describes the Meshery Model, a set of constructs that are used to represent and manage cloud-native systems.
Meshery’s internal object model is designed to provide a consistent and extensible way of capturing and characterizing the resources under Meshery’s management. Meshery Models serve as an exportable package to define managed infrastructure and their relationships, and details specifics of how to manage them.
Design Principles
Meshery Models adheres to several design principles, including establishing a set of constructs, clearly defining construct boundaries, allowing construct extension, reusing existing models, being user-centric, and simplifying complex networking and distributed systems. Meshery Models is designed to meet the following goals:
- Comprehensive: The model should be able to represent a wide range of cloud-native constructs, including applications, services, meshes, and infrastructure components.
- Extensible: The model should be extensible, allowing new constructs to be added as needed.
- User-centric: The model should be easy for users to understand and use.
- Machine-readable: The model should be machine-readable, allowing it to be used by automation tools.
Models as the Unit of Packaging
MeshModel supports packaging constructs as OCI-compatible images, making them portable and encapsulating intellectual property. Model packages can include multiple MeshModel constructs, facilitating reusability and versioning.
Model Packaging
Model constructs can be packaged and exported as OCI-compatible images. This makes them portable and allows them to be shared between different environments.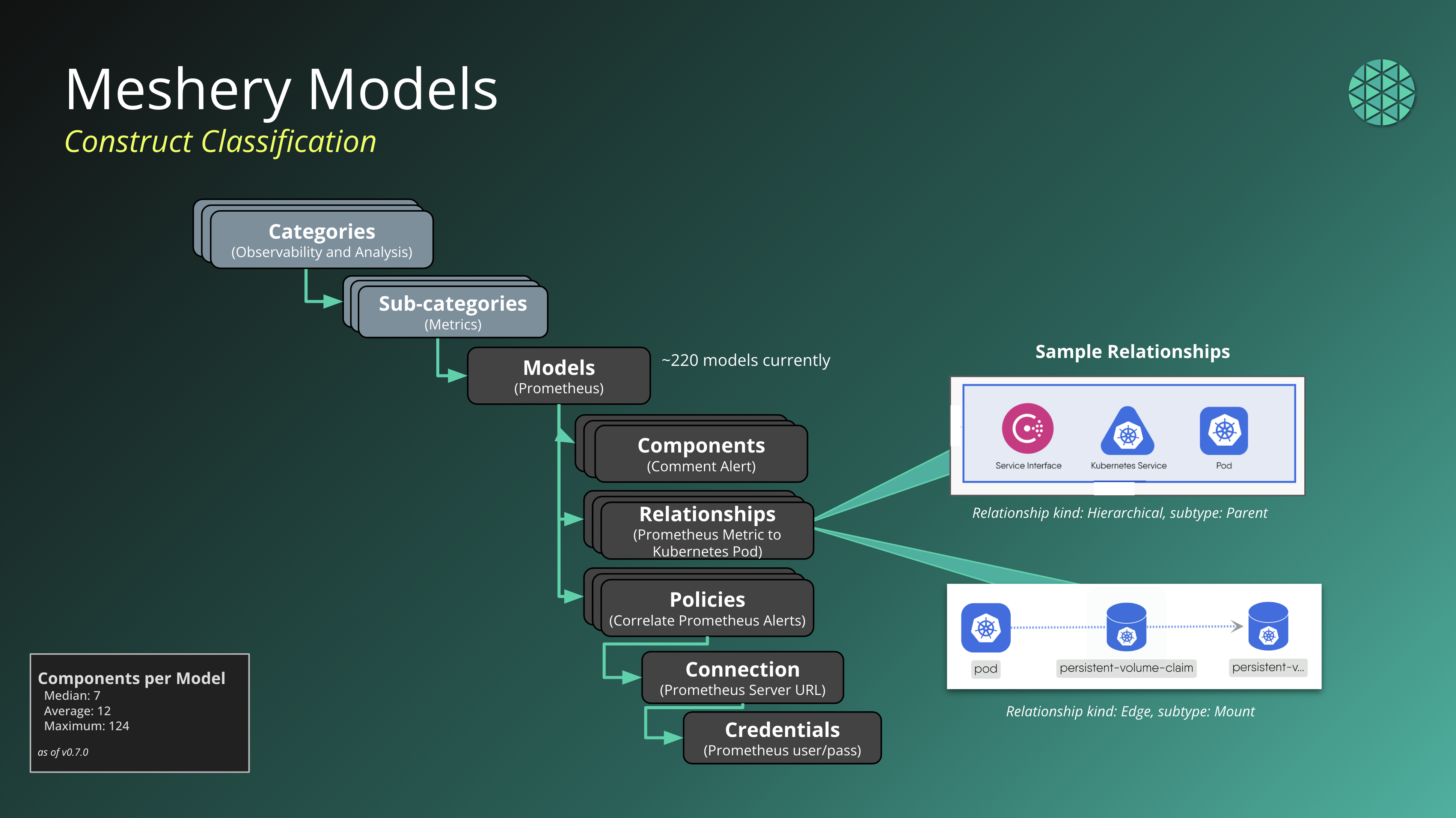
Key aspects and characteristics
You might not fully comprehend the Meshery Models figure above. The following analogy offers an alternative viewpoint from which to comprehend the Capabilities Registry (where Models are imported and their capabilities registered for use).
Models
Models introduce various core constructs that form the foundation of the model. Some of the core constructs mentioned in the document include Components, Designs, Policies, and Relationships. Models having the same name and version attributes are considered duplicates.
Component
Components represent entities in the Meshery ecosystem, exposing capabilities of the underlying platform. They can be registered, created, and used by users and operators. Components have definitions, instances, and associated metadata. Components having the same kind, apiVersion and model.name attributes are considered duplicates.See Relationships in GitHub for more information.
Designs
Designs are deployable units in Meshery that describe the desired infrastructure. They consist of components and patterns, allowing users to define and configure the behavior of their cloud-native applications. A design is a collection of components and patterns that represent a desired state of infrastructure. Designs are used to deploy and manage cloud-native systems.
Patterns
A pattern is a reusable configuration that can be applied to components or designs. They define best practices for configuring and operating cloud-native application functionality. Patterns can be applied to components or designs, and they are read-only.
Metadata
Metadata provide additional details about a component in Meshery. They offer specific functionality or characteristics associated with a component, enhancing its capabilities. Metadata can be attached to components to customize their behavior.Policy
Policy includes constructs for managing metrics, defining actions, and specifying color properties of components or designs. These constructs help in monitoring, controlling, and visualizing different aspects of the Meshery ecosystem. See Policies in GitHub for more information.
Relationships
Relationships define the nature of interaction between interconnected components in MeshModel. They represent various types of connections and dependencies between components, such as hierarchical, network, or default relationships. Relationships have selectors, metadata, and optional parameters. See Relationships in GitHub for more information.
Evaluation of Relationships
Meshery provides a relationship evaluation algorithm to ensure desired behavior enforcement. Policies can be applied to components and relationships, defining rules and actions based on predefined conditions.
Model Schema
Model constructs are defined using a schema language called Cue. Cue is a powerful and expressive language that is well-suited for defining cloud-native constructs.Conclusion
The Meshery Model is a powerful and flexible tool for representing and managing cloud-native systems. It is designed to meet the needs of both users and automation tools, and it is extensible to meet the changing needs of the cloud-native ecosystem.
Next Steps
The Meshery team is currently working on the following:
- Extending the model to support additional constructs
- Improving the tooling for working with the model
- Integrating the model with other Meshery components
We encourage you to get involved in the development of Meshery Models and to share your feedback.
